Sea Creatures in your Neighborhood
Who’s up for a little marine-inspired scavenger hunt? Get ready for NJSGC’s “Sea Creatures in your Neighborhood” campaign! Here’s the plan.
- Draw and color a picture of NJSGC’s “animal of the week” (more information below).
- Include a “fun fact” about this creature.
- Hang your masterpiece in a front window, door, or yard. Snap a photo to post on social media with the hashtags #SeaCreaturesInYourNeighborhood, #NJSGC, and #SeaGrantSTEM. Be sure to include the name of your city or town. Feel free to send photos directly to NJSGC by contacting our Communications Specialist.
- On your next ride or walk around the neighborhood (while respecting the rules of social distancing), take pictures of any #SeaCreaturesInYourNeighborhood you notice. Or search and discover more virtually.
- Encourage friends and family to do the same and be sure to share your findings with us!
- Stay tuned for next week’s ”animal of the week” and repeat. Stay safe and have fun while learning about our favorite sea creatures found along the Jersey Shore!
- NJSGC will “spotlight” all submissions throughout Spring 2020.
__________________________
June 22, 2020
The Long-Clawed Hermit Crab (Pagurus longicarpus) – please use this template for guidance.
Have you ever walked through a shallow, intertidal beach and noticed a small, dark object moving along the sandy bottom? If so, chances are that you’ve seen a long-clawed hermit crab, one of many marine crustaceans found along the Jersey shore. A close relative of lobsters, long-clawed hermit crabs are invertebrates with exoskeletons that shed in order for the animal to grow. Like lobsters, long-clawed hermit crabs have two chelipeds (claws). but instead are narrow and unequal in size, with the right one growing larger than the left. They have five pairs of legs and use the first three pairs for walking; the fourth and fifth pairs are small and modified to hold into the gastropod (snail) shell that they carry on their backs. Hermit crabs “wear” unoccupied gastropod shells to protect their soft, elongated abdomens and will change shells when they outgrow the current one.

New Jersey Fish and Wildlife (fact sheet)
Did you know…
1. Hermit crab eggs hatch into larvae, called zoea. After molting several times, the zoea become megalops which then develop into juveniles, which will then grow into adults.
2. Long-clawed hermit crabs are the ultimate recyclers because, as scavengers, they recycle energy back into the ecosystem.
3. Long-clawed hermit crabs can regenerate lost limbs when they molt.
Check out this cool video of a long-clawed hermit crab changing shells with anemones. And here’s another clip of hermit crabs living in aluminum cans.
June 5, 2020
The Atlantic Silverside (Menidia menidia) – please use this template for guidance.
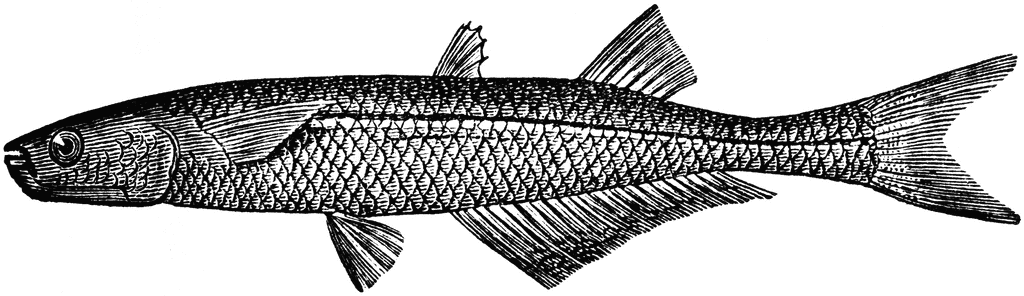
The Atlantic Silverside is a resident species and is one of the most abundant fish found in NJ’s estuaries and nearshore habitats. They have long slender bodies that are grey-green above and pale colored below with a distinct silver band that runs along each side (giving it the name “silverside”). Silversides are small, growing only up to 6 inches in length, and can often be found schooling in shallow waters. Commonly called “spearing” or “shiners” by fishers that use them for bait, silversides are consumers in the marine food web because they feast on the tiny phytoplankton and zooplankton that drift with the currents. Their small mouths lack teeth and are positioned upwards at the end of their snouts so that they can grab food that floats or swims above them. Females are usually larger than males and during the spawning season (May, June, early July) will deposit egg clusters on sandy bottoms. Silversides are sensitive to fluctuations in salinity, dissolved oxygen, and temperature, so they are an important species in helping scientists study environmental change.
Did you know…
-
Atlantic silversides can live up to two years, but most only make it to one year.
-
Silverside eggs that hatch in cooler water will develop into females, and those that hatch in warmer water will develop into males.
-
Silversides are an important food source for other marine animals in the estuary, and are eaten by everything from bluefish and striped bass to sea birds and crabs.
May 22, 2020
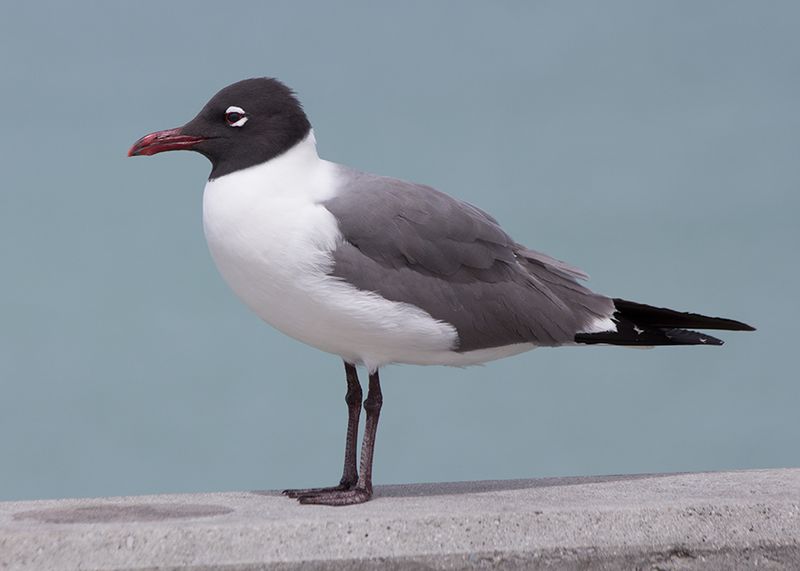
The Laughing Gull (Leucophaeus atricilla) – please use this template for guidance.
“Memorial Day is the start of the beach season at the Jersey Shore, and no sound is more iconic to beachgoers than the call of the laughing gull (click on this link to hear one). Like many vacationers, laughing gulls are regular visitors to NJ’s beaches, marshes, and back bays throughout the summer and fall. These medium-sized birds are relatives to lesser black-backed and Bonaparte’s gulls, which they can be found in congregation with along coastal areas of NJ. Adults have black heads, thin white eye crescents, and red bills which make them easy to identify. If you notice a laughing gull extending and lowering its neck, calling, and then throwing its head backwards, it is displaying a threatening behavior and alerting other gulls to stay away. This is also an important reminder for all beachgoers to practice social distancing!”
Did you know…
– Laughing gulls are opportunistic feeders. They eat snails, insects, crabs, squid, garbage, and anything else they can get their beaks on – including the snacks they steal from your beach bag!
– During the spring nesting season, male and female laughing gulls build their nest together where the female will lay 2-4 brown with black-speckled eggs.
– The oldest known laughing gull lived to be 22 years old!
Check out this cool video – and happy Memorial Day weekend!
May 11, 2020
The Common Atlantic Octopus (Octopus vulgaris) – please use this template for guidance.
“In honor of Mother’s Day this past weekend, we would like to pay tribute to one of the most dedicated moms in the ocean, the octopus! The Common Atlantic Octopus can be found living in crevices and muddy bottoms of NJ’s coastal waters. This member of the Mollusk family has greyish-yellow or brownish-green smooth skin that can change with its surroundings, which helps it maintain its private lifestyle. Like all octopuses, it has 8 arm-like tentacles with suckers to capture its prey. When a female is ready to lay her eggs, she will find a hiding spot such as a hole or other hollow area that can be sealed off with rocks, shells, or debris. Inside she will lay thousands of eggs (up to 500,000!) and stitch them together in long braids that she will then attach to the walls of the den. In the 4-5 months that it takes for the eggs to hatch, the mother octopus never leaves the nest to feed. Instead, she will vigilantly care for her young by carefully blowing water with her siphon over the eggs to keep them clean and oxygenated and protecting them from predators. After her young have hatched and she has shuttled them out of their nest, she will finally venture out in a weakened state and give the ultimate gift – her life.”
Watch this cool video excerpt from PBS’ “Nature” show entitled Octopus: Making Contact where a teenager befriends this unique creature!
Did you know…
– Considered the smartest of all invertebrates thanks to their large brains, octopuses can recognize people and explore objects through play – even opening jars and locked boxes!
– Octopuses use their tentacles not only for touching but for tasting, too!
– The Common Atlantic Octopus can grow up to 3 feet and live for 2-3 years.
– As a mollusk, octopuses are related to clams and oysters, but they have no external or internal shell.
May 1, 2020
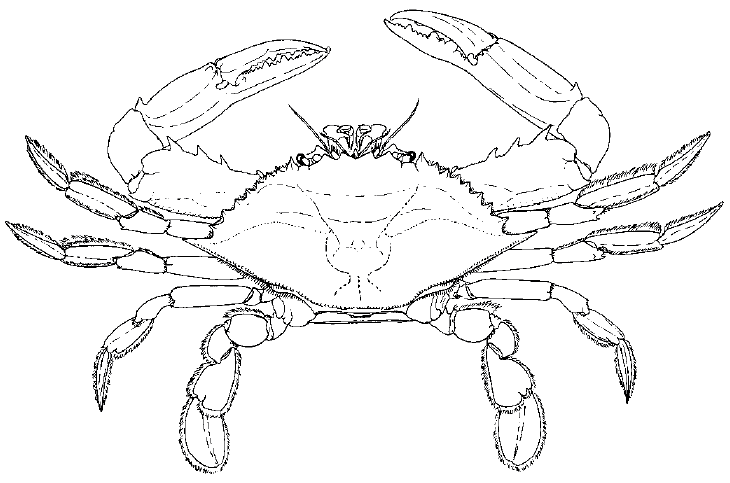
The Blue Claw Crab (Callinectes sapidus) – please use this template for guidance.
“Spring is a time that many land animals emerge from hibernation, and there are some similarities in the ocean. Although most marine organisms do not hibernate specifically, some (like the blue claw crab) spend the colder months buried in the ocean bottom in a dormant state. As the duration of sunlight increases and water temperatures rise in May, hungry blue crabs will emerge and swim to shallow bays and estuaries. Crabs are ambush predators and once close to shore they will lie in wait for their prey to swim or amble by. Eating clams, fishes, and other crabs cause these invertebrates to fatten and eventually molt as they outgrow their shells. It takes a few hours for the new shell to harden, and while it is “soft shell” a crab is vulnerable to predators. Therefore, blue crabs will once again bury themselves into the sandy shallow bottom until their shells can protect them.”
Did you know…
– Blue crabs are only one of two crab species in NJ that can swim – their 5th pair of (back) legs are modified to look like paddles, known as swimmerets.
– By looking at the abdomen, you can tell the gender of a crab: males are shaped like a golf tee, while females are shaped either like a triangle (immature) or rounded (mature). The large claws on mature females also have red tips.
– Although crabs spawn in the fall, females do not lay eggs until the spring, and they can lay up to 8 million at a time!
– Male blue crabs can live up to 3 years while females only live up to 2 years.
– Blue crabs feed by catching prey with their large claws and ripping their food apart to pass into their mouths.
Check out these cool videos!
Blue Crab Biology (University of Georgia Marine Extension and Georgia Sea Grant)
Local Crab Fishery (NJTV News)
April 24, 2020
In honor of NJSGC’s virtual launch of our “Sharks vs. Rip Currents” program…
The Atlantic Spiny Dogfish (Squalus acanthias) – please use this template for guidance.
“The Spiny Dogfish is a small shark found in abundance throughout the Garden State’s coastal waters. They are called ‘spiny’ because of the long spines located anterior to each of its two dorsal fins. These slim fish have long snouts and can grow up to four feet long. Like many sharks, Dogfish exhibit countershading, a type of camouflage that makes them effective predators. Dogfish are grey with white spots on their dorsal sides, and white below (on their ventral sides), making them difficult for prey swimming below them to see in the water. They are opportunistic feeders, which means that they will eat just about anything that they can catch, but they prefer crustaceans, squid, jellyfish, and other fish. While they are predators, Spiny Dogfish are also eaten by other animals higher up the food chain such as cod, hake, sharks, and even some whales. Dogfish, together with all types of sharks, are very important to the marine food web by helping to keep other species populations in balance.”
Did you know…
– Many people in European countries enjoy eating dogfish as part of a “fish and chips” meal.
– Females take up to 12 years to mature. When they do, they can give birth to an average of 6 live pups that take up to 24 months to gestate.
– The dogfish’s salt gland produces a substance called squalamine which scientists are studying as an anti-cancer agent.
– Spiny dogfish can live up to 40 years.
Check out this cool YouTube video on shark conservation.
April 17, 2020
The Osprey (Pandion haliaetus) – please use this template for guidance.
“Sometimes called “fish hawks,” ospreys live along waterways, lakes, and coastal waters in NJ and are typically spotted throughout Spring/Summer/Fall. These large birds feed almost exclusively on fish and can plunge feet-first into water to catch prey with their sharp talons. Identifiable characteristics of the osprey include: dark brown back, white front plumage, dark stripes on the head and tail, bent wings, and a high-pitched call.
Ospreys breed during this time of the year, and pairs can be found preparing for nesting. Nests need elevation to keep predators away, so observers are likely to find them in tall trees, chimneys, cell phone towers, or man-made nesting platforms. Ospreys use sticks, bark, seaweed, bones, and even beach towels to build their nests. Males collect nesting materials while the females arrange it. The couple will then use this same nest for years to come – eventually even ‘growing’ large enough for a human to sit in!”
Did you know…
– Ospreys mate for life, but males and females winter separately.
– Females are larger than males and have a dark feather “necklace” on their white chest.
– Females lay approximately three brown-spotted eggs in mid-April to early May, and chicks hatch in late May.
– Both osprey parents help feed and care for their young.
Thanks to the Conserve Wildlife Foundation of NJ, fans can now watch the live action Barnegat Light Osprey Cam.
April 10, 2020 (Easter Edition)
“Egg case of the Jersey Shore,” the Clearnose Skate (Raja eglanteria). Please use this template for guidance.
“Have you ever seen a dark brown, leathery pouch with “horns” on each end wash up on the beach? You might have heard it being called a “mermaid’s purse,” but it doesn’t come from a mermaid at all! They’re actually made by skates, a flat fish related to sharks. Female skates produce these casings when they lay their eggs and attach them to seaweed. The young grow and develop inside these egg cases, eventually breaking out and swimming away when they get to be about 6 inches long, which can take up to 3 months. As they mature, they feed on shrimp and other crustaceans, mollusks, and small fish.”
Did you know…
– Skates have cartilage instead of bones.
– Skates have flattened bodies, with their pectoral fins joined to their head and trunk, and a long tail trailing behind them.
– Skates can’t harm people with their tails because they do not have a venomous barb like stingrays do.
Additional Resources:
– Clearnose skate “walking” behavior (video)
– Little skate hatching (video)
APRIL 3, 2020
The Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectus) – please use this template for guidance.
“The lined seahorse is a resident of NJ’s shallow coastal waters and can be found living in eelgrass and seaweed beds. This fish has a horse-like head with a small mouth at the end that can quickly slurp up its favorite food – tiny crustaceans and other zooplankton. Its body is upright and covered in bony plates, and its long, finless tail curves inward to help it grasp objects. Seahorses grow to be 4-6 inches in length and can live to up to 4 years in the wild. They are vulnerable to pollution, loss of habitat, and overfishing (people like to collect them!) so protection is important so that they can thrive in their natural environment.”
Did you know…
– Seahorse fathers incubate the mother’s eggs and give birth to as many as babies!
– Seahorses mate for life, and pairs “dance” together every morning.
– Their color varies from light brown to almost black and it can change depending upon the background it is against.
Additional resources:
The Maritime Aquarium
Chesapeake Bay Program
National Geographic
Scripps Institution of Oceanography
MARCH 27, 2020
NJSGC’s first pick of the week is the Eastern Common Sea Star. Feel free to use this template for guidance.
Did you know…
– Sea stars can regenerate their limbs if damaged or severed
– Sea stars eat their food outside of their body by turning their stomach inside out and extending it through their mouth
– Sea stars can live up to 35 years
– Or do your own research and get creative with the “fun fact!”
“The Eastern Common Sea Star is native to NJ’s coast and can be found in shallow rocky areas or sandy bottoms. Usually referred to as ‘starfish,’ they’re actually not fish at all. They’re echinoderms, belonging to a group of marine animals with tough, spiny skin and no bones (invertebrates). Sea stars have limbs (called rays) that radiate out from a central disc (radial symmetry) in multiples of five that help them move around and find food. They are carnivorous predators that love to eat snails, clams, oysters, mussels and barnacles. Sea star colors vary from olive, brown, yellow, orange, purple ,or red. They are related to sand dollars and sea urchins, both of which can also be found in coastal NJ waters.”
—
Stay tuned for next week’s creature!